The Future of Construction: Understanding Prefabricated Buildings
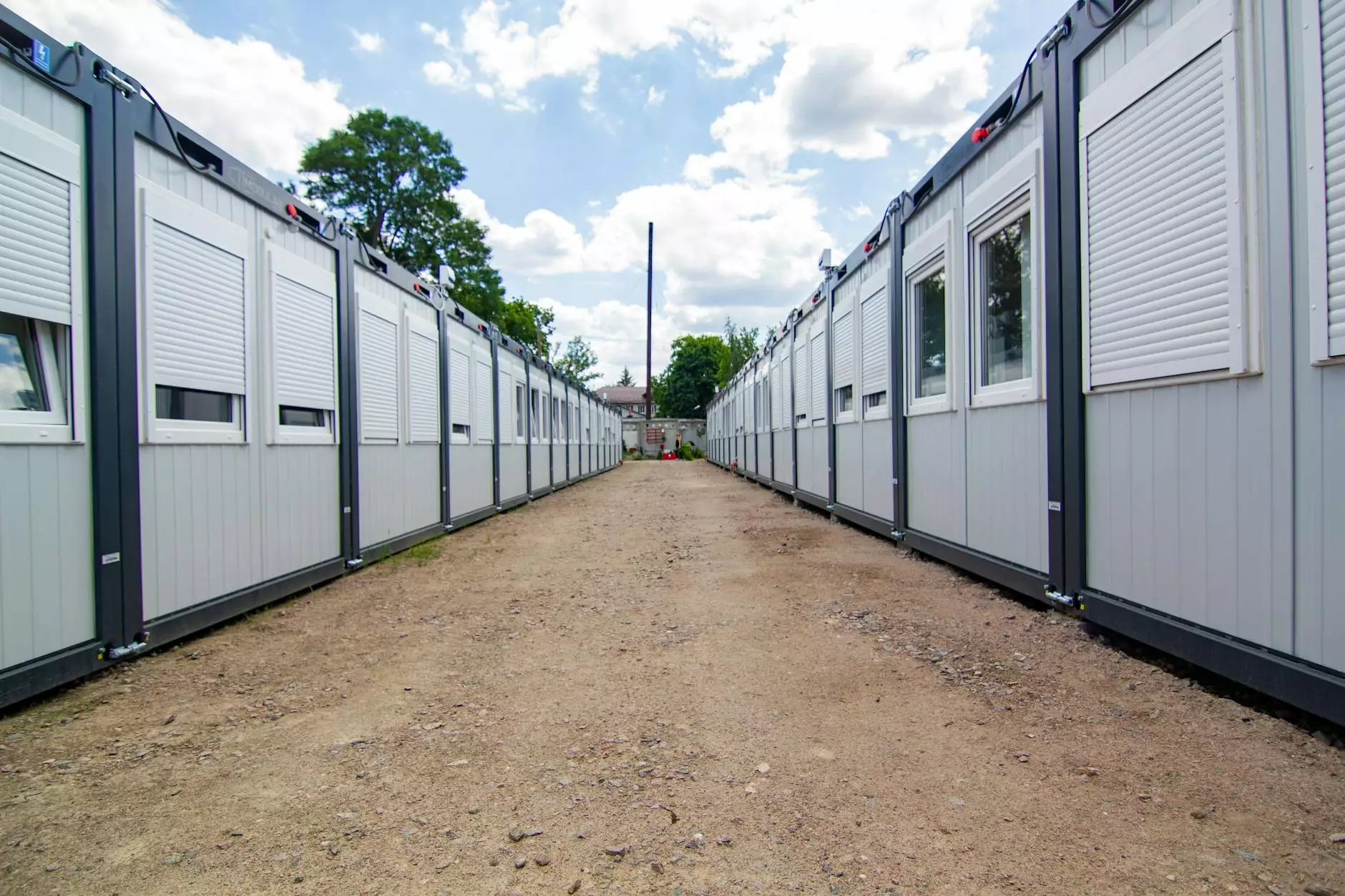

Prefabricated buildings are revolutionizing the construction industry. From residential houses to commercial spaces, the demand for efficient and cost-effective building solutions is on the rise. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects that make prefabricated buildings a popular choice among contractors and developers, with a focus on the benefits, designs, and innovations that are shaping this domain.
What are Prefabricated Buildings?
Prefabricated buildings, often referred to as prefab structures, are constructed using pre-manufactured components or modules that are produced off-site in a factory setting. These components are then transported to the construction site and assembled to form a complete structure. This approach contrasts with traditional construction methods, where the building is constructed entirely on-site from raw materials.
Key Elements of Prefabricated Buildings
- Standardization: Many prefab components are standardized, allowing for mass production and reduced costs.
- Modularity: Buildings can be expanded or modified easily by adding or removing modules.
- Efficiency: Reduced construction time due to simultaneous site preparation and component manufacturing.
- Quality Control: Factory conditions allow for better quality assurance processes during production.
Advantages of Prefabricated Buildings
Opting for prefabricated buildings offers numerous benefits that appeal to both contractors and clients. Here are some of the most compelling advantages:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
One of the standout benefits of prefabricated buildings is their cost-effectiveness. Reduced labor costs, minimized waste, and efficient use of resources contribute to significant savings. Additionally, the shorter construction time translates to faster project completion, which allows for quicker returns on investment.
2. Speed of Construction
With prefabricated building systems, the time taken from conception to completion is drastically reduced. While traditional building methods can take months or even years, many prefab projects can be finalized in a matter of weeks. This rapid turnaround is particularly beneficial for businesses that need to set up operations quickly.
3. Environmental Impact
As sustainability becomes a pressing issue, the construction industry is shifting towards practices that minimize environmental impact. Prefabricated buildings often have a smaller carbon footprint due to their efficient production processes. Moreover, the controlled manufacturing environment limits waste, and many components are recyclable.
4. Design Flexibility
Modern prefabricated buildings offer a high degree of customization. Architects and designers can create unique layouts and finishes, making it possible to cater to diverse aesthetic preferences and functional needs. From modular homes to commercial spaces, the ability to tailor spaces has never been easier.
5. Strength and Durability
Contrary to some misconceptions, prefabricated buildings are incredibly strong and durable. The materials used are engineered for resilience, and the precision of factory production reduces the likelihood of construction flaws, ensuring that these structures can withstand various environmental conditions.
Innovations in Prefabricated Building Technology
The evolution of prefabricated buildings has been driven by advancements in technology. Here are some of the innovations that are enhancing the quality and appeal of these structures:
1. Advanced Materials
Modern prefab buildings utilize cutting-edge materials, including engineered wood, steel, and energy-efficient insulation systems. These materials not only enhance the strength and durability of the building but also improve insulation and energy efficiency, leading to lower utility costs for occupants.
2. Smart Technology Integration
Today’s prefabricated structures can seamlessly incorporate smart technologies. From automated lighting and heating systems to integrated home security solutions, owners can enjoy a level of convenience and control that was previously unattainable in traditional constructions.
3. Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a hallmark of the prefabricated building industry. Innovations such as solar panel integration, green roofs, and rainwater harvesting systems are being embedded in design and construction practices, making these buildings environmentally friendly.
4. 3D Printing
3D printing technology is making waves in the prefabricated building sector. By creating components layer by layer from digitized models, construction becomes more efficient, and custom elements can be produced with minimal waste. This innovative approach is set to further revolutionize how prefab buildings are designed and constructed.
Applications of Prefabricated Buildings
The versatility of prefabricated buildings allows them to be used in a variety of contexts. Here are some common applications:
1. Residential Homes
One of the most popular uses of prefabricated construction is in the residential sector. Homeowners are increasingly opting for prefab homes due to their affordability and customizable designs. These structures can vary from modest single-family homes to elaborate multi-story buildings.
2. Commercial Spaces
Businesses are recognizing the benefits of prefabricated buildings for office spaces, retail stores, and service locations. The quick setup and adaptability of these structures make them ideal for various business needs, including pop-up shops and expandable office layouts.
3. Educational Facilities
Schools and educational institutions are utilizing prefab buildings to address space shortages. Temporary classrooms and permanent facilities can be built quickly and efficiently, providing essential services without compromising on quality.
4. Healthcare Facilities
In times of urgent need, such as during public health emergencies, prefabricated buildings can be deployed to create temporary hospitals and clinics rapidly. Their flexible design can accommodate various healthcare functions, from patient rooms to laboratories.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of prefabricated buildings are numerous, there are challenges that stakeholders should consider:
1. Initial Costs
Despite long-term savings, the initial investment for prefab construction can be higher than traditional methods, particularly in areas where land and site development are expensive. Understanding the full scope of costs is crucial for informed decision-making.
2. Site Limitations
Not all construction sites are suitable for prefabricated buildings. Factors such as site access, local zoning laws, and the logistics of transporting large components must be carefully evaluated to ensure project viability.
3. Building Codes and Regulations
Compliance with local building codes and regulations is essential and can sometimes pose a challenge for prefabricated structures. Working with experienced contractors familiar with these regulations can help navigate potential issues.
Conclusion: The Future is Prefabricated
In summary, prefabricated buildings are a forward-thinking solution that addresses many of the challenges facing the modern construction industry. With their blend of efficiency, sustainability, and design flexibility, they provide an innovative alternative to traditional building methods.
Module-T stands at the forefront of this exciting transformation, offering high-quality prefabricated building solutions tailored to contractors and building supply needs. As a contractor considering a project, exploring the potential of prefabricated buildings could allow you to deliver faster, more sustainable, and cost-efficient structures to your clients.
Embracing the future of construction with prefabricated buildings not only enhances your business's capabilities but also positively impacts the environment and community. By prioritizing innovation, sustainability, and efficiency, you can take full advantage of everything prefab construction has to offer.